According to Ian Somerville, Emma Wood, Mark Gillham the authors and researchers of this journal. The purpose of this article is to present and discuss the results of research conducted among Scottish communication professionals, which investigated their perception of and attitudes toward recent trends and future developments with respect to the free organisational publication which is the use of new media in the public relations world.
In this article, they finds that first, there have been significant changes in purpose, content, design and distribution of free organisational publications in recent years, but for the predictable future communication professionals foresee important roles for both print and electronic organisational publications. Secondly, practitioners tend to adopt the rhetoric and language of “technological determinism” when discussing new media technologies. That is, they tend to see themselves as relatively powerless in the face of “technological advances” and see their role as simply adopting what is given to them. This article argues that viewing the technology/society relationship from a more “social shaping” perspective will allow practitioners to utilise new media technologies in ways which will benefit them and their stakeholders.
This article also provides a more complete picture of the “value” of free organisational publications and also draws lessons for practitioners on how best to employ print and electronic publications and how they should respond to current claims made about new media technologies.This article is to conclude what is, in many ways, a quite different new media environment from that analysed by other researchers regarding this matter. This study also theorises practitioner discourses in a more comprehensive way than many earlier studies by examining them in the context of the theoretical debates surrounding the relationship between technology and society in the new media and public relations world.
https://www.issa.org/Library/Journals/2008/October/Ben-Itzhak-Organized%20Cybercrime.pdf
By Yuval Ben-Itzhak
According Yuval (2008) cybercrime has developed into a fast-expanding, global industry. Its operations closely resemble the real business world, including profit-driven organized cybercrime. Cybercriminals use an arsenal of highly-effective crime tools, deploying sophisticated Criminal-2-Criminal (C2C) business models for their operations, heavily borrowing and copying from the legitimate business world. These kinds of crime pros also use robust and scalable crimeware that gives them maximum flexibility in terms of command and control for stealing and trading data. Cybercrime attacks are made easy due to the availability of crimeware toolkits. These toolkits are “how to…” software packages that instruct users step-by-step how to infect a system, followed by how to retrieve data for financial gain. Crimeware toolkit creators also deploy Crimeware-as-a- Service (CaaS). A classic example is the notorious NeoSploit toolkit that contained a delivery system for the Trojan upon a successful exploitation.
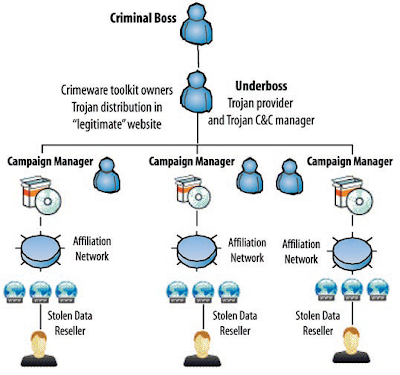
The damage for both organizations and individuals resulting from successful crimeware attacks is widespread and long-lasting – no organization, company, enterprise or business with Internet access is safe. This vision is confirmed by Marcus Alldrick, responsible for information protection and continuity at Lloyd’s. He pointed out that targeted attacks perpetrated by organized crime are on the increase due to the high return on investment. Fighting cybercrime is problematic in many aspects. In contrast to classic crimes such as drug offences or fraud, cybercrime has a vast scope, consisting of all kinds of actions designed to steal data for profit. Location is a problem as well; crimeware servers are often in a different country than the criminals that operate them.
By SITI FARAH LINA BT ABDUL RAHIM
2008285658
MC22S5A
Please be informed that our individual assignment for New Media (Shell) is DUE TOMORROW 3rd NOVEMBER 2010..
So, do submit your assignment as soon as possible at Miss Baby offices and mail the soft copy to her, just in case..(anusharin@gmail.com).
No marks will be given after the dateline..
Thank you;)
This article is about the nature of young people’s relationship with technology and effort to explode a few myths about their affection for it. Rolfe. J and Gilbert. M, 2006 said in their article that young people have a natural affinity for digital technology they also have become totally dependent on it and becoming alienated from each other because of their addiction to it. Because of that it is causing them irreparable damage in all manner of disgusting ways.
In their study they found that accessibility and usage of digital technology is a class issue, which is the lower classes are far less likely to have information or communication technology at home and particularly at the workplace. This means that the middle class parents are much more likely to be net-savvy and so able to support their children in this respect. Rolfe. J and Gilbert. M, 2006 also found in their study that young people are constantly busy socializing, consuming and entertaining themselves using the new media. Most of them do not love technology by itself but they view it as a facilitator that enables them to communicate or entertain themselves. Besides, they are not addicted to technology but to communication. Communication is entertainment for this group so they need the technology to be as personalized, easy and instantaneous as possible.
Rolfe. J and Gilbert. M, 2006 also come out with several myth and reality about young people and technology in their research. There are:
Myth – Conventional wisdom says that all young people are ‘Digital Natives’. ‘Digital Natives’ are those who have grown up with Digital Technology, ‘Digital Immigrants’ are those who have only come to Digital Technology in adulthood. But in the reality – Adults are often ‘Digital Immigrants’ and therefore perceive all young people to be ‘Digital Natives’. However, young people are not all tech-savvy. The researcher found that 20% say young people actively avoid using Technology, while the vast majorities are massively into communication & entertainment, with new technology merely being the facilitator.
Myth – The popular belief is that Digital Technology has democratized information and that young people are now one free-flowing global village. But in reality – Many young people are excluded from the digital revolution, for example rural youth (who use internet as an information source not for communication), people from lower class and certain ethnic minorities. New Technology incorporates rather than hide existing forms of youth culture.
Myth – Most adults presume that young people have more of an affinity with Technology than previous generations, because they learn all about IT at school. But in reality – In fact IT lessons are very ordinary. They focus on file management, Word, Excel and other basic skills. Many young people use more complex programs at home so it makes school seem out of touch. In this survey, the researcher also found the percentage on how the young people learn the technology, the result are from friends 71%; what I teach myself 67%; school 44%; and family 41%.
Myth – Young people use new Technology in a way that is complex and impenetrable to older generations. In reality – Most Technology use is actually rather ordinary and just strengthens existing interests. Youth reach their technological peak around their mid 20s and due to increased resources and accessibility at that age. In their study also found the percentage of the reasons young people use the internet most frequently. There are: to communicate with friends by e-mail (85%); random surfing (82%); shopping (79%); to communicate with friends via Yahoo/MSN,(60%); online banking (59%);research for work/college (56%); and downloading music (53%).
Myth – New media creates generations of isolated, alienated youth. In reality – The home was traditionally the domain of the family. Now, friends have a ‘permanent presence’ in the home (via mobiles and MSN). Beside Young people have a real need for constant contact and ‘micro-tending’ their relationships so they are constantly using technology to arrange their social life.
As a conclusion, the internet has become much more trusted communication channel among young people nowadays. Young people increasingly take information, downloading the video and music, play games and socializing with their virtue friends from the internet. However, it depends on young people to use the internet appropriately and responsibly in their daily life.
ZAIDATUL HANIM BINTI ALIAS
2008285668
Rolfe. J, Gilbert. M, 2006, youth, new media, technology and communication, Young Consumer, Quarter 2, www.emeraldinsight.com.
By: NURSYAFINAS BT. MOHD ZAHURI (2008285606)
Today’s topic is about e-commerce as a trend in business. The quick emergence of new media and technology has brought many individuals to set up a virtual shop as one way to market their products. Recently, one of our friends has launched her very own blogshop, AdoreLaMode, (hope all of you noticed this!) and I found that it has its own specialties in terms of managing it, compared to a real shop lot. Let’s discuss this into deeper.
BLOG/SHOP: it is authentic so don’t worry
The popularity and persistence of Blogshops raises ethical issues regarding the presentation of the female teenage owners’ “self” to others and the relationship they maintain with buyers and other owners. Based from this journal, written by Gordon Fletcher and Anita Greenhill, blogshop is defined as from a technology point-of-view as virtual shops that utilises hosted blogging systems. But this neatness of precision belies a series of complexities regarding Blogshop practice. From the researcher’s external ethic perspective the hosts can be identified as being fully immersed consumers endeavouring to maximise their consumption and purchasing power through the use of blogging, mobile phone and public transport technologies.
The blog aspects of the Blogshops themselves are not particularly distinctive for their style, they retain the general look and feel of an “amateurish” blog – long pages bloated with images inappropriately over-sized for web-delivery. However, some of the longer established Blogshops are increasingly adopting cleaner design principles and a more disciplined use of imagery.
There is generally less willingness for hosts to include their full photos with, instead, photos of torsos, obscured faces, hands and legs utilised as the platform on which to model the available items (Riegelsberger, 2003). Blogshops also make “generous” use of images taken from printed and online fashion catalogues and other Blogshops to complete their blog’s design
Blogshops increase a host’s economic independence and raises their cultural position among peers by obtaining the latest fashion items and desirable rare goods. The combination of sprees, meetups and the general quality of goods offered all raise the issue of trust on the behalf of both buyers and hosts (Teo and Liu, 2007). Many of the hosts are keen to identify the fact they are not “scammers” and that they blacklist any buyers who are identified as being such, both at their own blog and at other Blogshops within their close network.
The rapid development of Blogshops has enabled a commonality and evolution of individual experience enabled by a rich assemblage of technology, culture and location. Looking beyond the possibility of dismissing Blogshops as “just another” form of Web-based communication or social network.
This paper has illustrated that Blogshops offer the first level of insight into a complex anthropologically rich environment that brings together a form of economic need, locational circumstance, technological capacity. Blogshops offer significant insight into a broader series of contemporary cultural experiences including the meaning and extent of e-commerce and social networking, forms of globalised youth culture, the imprecise influences of the weakness of fashion and shifting mainstream attitudes towards self-representation.
.:.THE END.:.
P/S: Good luck for the final exams!!
Perhentian, di sini sejarah tercipta, di sini kami belajar sesuatu, di sini kami bahagia bersama dan ianya akan terus tersemat di ingatan. Perhentian, suatu tempat yang cukup indah, tiada kata dapat melafazkan keindahan yang tercipta. Terima kasih, inilah ungkapan teristimewa buat pengarah projek yang bertungkus lumus merealisasikan impian ini dan di pantau oleh Miss Melina Bt Mahpuz.
Akmariela Ahmad Sayuti
:)
Millennial Students Relationship With 2008 Top 10 Social Media Brands Via Social Media Tools
By :Alisa Lynn Agozzino
URL: http://etd.ohiolink.edu/send-pdf.cgi/Agozzino%20Alisa%20L.pdf?bgsu1262651087
This journal discussed about the Internet has become a major player in the public relations field within the last decade. The World Wide Web has served as a key contributor in how organizations and their publics develop mutually beneficial relationships, an important characteristic for public relations. With emerging social media tools such as Web 2.0, blogs, podcasts, wikis, and RSS technologies becoming more highly discussed topics within the field, the Internet itself has become a public relations toolbox that holds all the newest social media tools for every public relations practitioner.
When public relations practitioners do not take into consideration targeting their messages, those messages fall upon the mass society as a blanket with only hopes of the targeting audience being able to pick up the message. Social media tools could make or break hiring of public relations firms in the future.
This journal also highlight that not only Public relations practitioners who need an understanding of social media within the field but also PR educators in the United States are being advised by public relations practitioners to consider adopting social media into the curriculum.
Social media are changing public relations careers, whether the field is ready or not. Scott (2007) pointed out how social media have changed the look of public relations, beginning with the rise of the Web: PR is no longer just an esoteric discipline where great efforts are spent by companies to communicate exclusively to a handful of reporters who then tell the company’s story, generating a clip for the PR people to show their bosses.
Now, great PR includes programs to reach buyers directly. The Web allows direct access to information about your products, and smart companies understand and use this phenomenal resource to great advantage. As a conclusion, PR practitioners and educators should have a knowledge and skills on the new technologies in order to attracts and keep maintaining the power of PR itself, if not, PR will not survive in the end.
NUR AIN BT MOHD FAZALI
2008285558
The journal I took from website is “New Media: A New Medium in Escalating Crises? ” by Joanna Siah Ann Mei, Namrata Bansal and Augustine Pang. The researchers are from the Wee Kim Wee School of Communication and Information, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore. Crisis consider as a disaster for the company and it need for the company to handle effectively in order to solve it or prevent it from becoming worse. In the previous time, the crisis is been handled in a traditional way where as the company organize the press conference and it will be reported in the newspaper or in the magazine. Other than that, the issue sometimes have been filter by the gatekeeper and not literally knows by the publics in a deeply way.
As for today, with the highly technology been develop such as internet, it become the major medium for the company since the internet do not have the gatekeeper to filtering the information. This is the worse thing that can happen to the company that are trying to handle the crisis they been facing. Furthermore, it relate to the journal that I took consider that this new media escalate the message of the crisis for the company.
Most of companies today are uploading the crisis management in their website as a proof of their effort that they did in order to convince the constituents such as the investors, publics, government, media, employees and etc. Internet is the world without border and there a lot of sources to get the information. As for example, blogs, You Tube, social network, online publication and etc. Sometimes, there are a blogs that condemn the organization method in handling the crisis. For example, the BP Oil Spill in Gulf Mexico, there has a video upload by the Environmental Association that made fun of the company way in handling the oil spill. Furthermore, to make it worse, the publics also condemning the BP Company since they do not really committed in handling the disaster and the effects toward the nature and the animals habitat in Gulf Mexico.
It is one example on how the new media escalating the crises. As for the company, they should aware with this situation and mange the crisis in organizes and they should also consider every aspect of the impact of the crisis. Always come out with the press release and give the statement on what they did to overcome the crisis. This is the way to ensure the satisfaction the parties involve with crisis either in direct or indirect way.
SITI HANISAH BINTI MOHD ALI
2008285576
The article taken from www.emeraldinsight.com